Soaps these are the sodium and potassium salts of fatty acids, containing 10-22 carbon atoms in the molecule, showing detergency in aqueous solutions.
The term "soap" is also used in a more general sense to refer to fatty acid salts with other metals. In such cases, please specify in detail, that it is e.g.. calcium soap, magnesium.
Washing ability, in addition to the sodium and potassium salts of fatty acids, also show sodium and potassium salts naphthenic acids i resin.
Soap is an essential ingredient in personal care products, whose primary purpose is to effectively remove dirt from the body surface. It is also used for the production of detergents and used as the so-called. technical soap.
Getting soap
Soaps are obtained by two methods:
— by the action of alkalis on fatty acids;
— by saponification of fats with sodium and potassium hydroxides and carbonates.
Fatty acids are organic acids composed of hydrocarbon chains and the so-called. carboxyl group -COOH, at the end of the chain.
The fatty acid hydrocarbon chains differ in length, i.e.. the number of carbon atoms making up the chain, and the number of unsaturated bonds, so doubles (sometimes triples) between the carbon atoms that make up the chain. Fatty acids, which in practice most often make soaps, there are acids:
— stearynowy C17H35COOH, saturated,
- palmitic C15H31COOH, saturated,
— myristic C13H27COOH, saturated,
— lauric c11H23COOH, saturated,
- oil C17H33COOH, insatiable (one double bond),
— linoleic C17H31COOH, insatiable (two double bonds),
- linolenic C17H29COOH, insatiable (three double bonds). The chemical formula of a fatty acid can be written in the form
simplified as R-COOH, where R is the hydrocarbyl chain of the specified fatty acid.
If the fatty acid is treated with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), then soap is formed by the reaction:
R-COOH + NaOH = R-COONa + H20
The R-COONa sodium soap is therefore the sodium salt of a fatty acid. The preparation of potassium soap by treating a fatty acid with potassium hydroxide can be described analogously (KOH).
In practice, soaps are mainly obtained from natural fats, as fatty acids are not present in free form in amounts, that could satisfy mass production, while obtaining them from other raw materials is too expensive.
Fats are esters of fatty acids and glycerin.
Depending on the type of fatty acid, from which the fat is formed, it differs in melting point and consistency. Fats can be solid and liquid. Liquid fats are called with oils. Solid fats are esters of saturated fatty acids and glycerin, while oils are esters of unsaturated fatty acids and glycerin.
Natural fat is a natural composition of various fatty acid esters and glycerin.
Depending on the content of the individual components of this composition, natural fat has different properties. Natural fats are divided into animal and vegetable. Animal fats belongs to solid fats, because they are mainly composed of saturated hydrocarbon chains. Vegetable fats they are oils, because they contain unsaturated hydrocarbon chains.
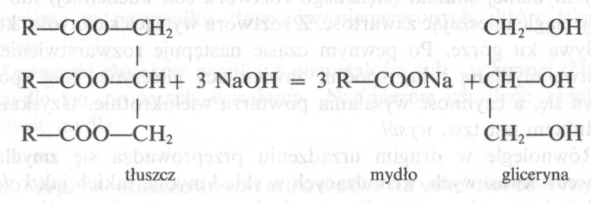
Glycerin is a by-product of the saponification reaction (trihydric alcohol), a valuable raw material in the production of cosmetics.
The properties of soaps obtained from natural fats differ depending on the raw fat used in the saponification process.