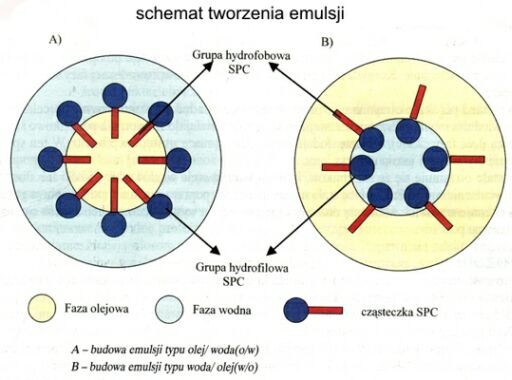
 Surfactants.
Surfactants.
From several hundred classes of known surfactants (SPC) industrial application has found 40 group, being dominant, except soap, only has 5 groups of these chemical compounds. Belong to them:
- straight-chain alkyl benzene sulphonates (LABS),
- fatty alcohol alkoxylates (AE),
- alkoxylated alkylphenols (APS),
- alkyl ether sulphates (AES),
- alkyl sulphates (AS).
The anionic SPCs are LABS, AES, AS, while non-ionic SPCs include AE and APS. Anionic agents currently predominate in applications (ok. 60%), then non-ionic (ok. 30%), an increase in the share of non-ionic funds is forecasted.
The most important anionic SPCs, produced for many years and in large quantities, are LABS. They are characterized by excellent surfactant properties, low price, easy to incorporate into liquid and powder media. Currently, there is a decrease in LABS consumption in Western Europe, and growth there, where consumption is low, i.e.. in China, India, Southeast Asia–Eastern.
AES has a high surface activity, high foaming capacity, good resistance to water hardness and temperature, they are gentler on the skin than LABS and AS. The greatest amounts of AES are used in shampoos, washing and bath liquids.
AS exhibit excellent surfactant properties, wetting, foaming and creating a stable foam. Their use, however, is limited, because they are sensitive to hard water, temperature, and their effect on the skin is slightly irritating. AS is better biodegradable than LABS, therefore they are eagerly used in washing powders in mixtures with other SPCs.
AEs have the largest share in the non-ionic SPC group. These compounds show very good wetting and surfactant properties with moderate foaming properties. They are virtually compatible with all SPCs, while the performance on the skin is comparable to that of most SPCs. They are often used in washing powders and liquids, household cleaners and play a large role in municipal and industrial applications.
APS is hygroscopic, have a mild effect on the skin. Due to the lower biodegradability compared to AE, their use in household chemicals is limited. APS are mainly used in industry.
Many relationships are developed, which are regarded as substitutes for the most commonly used substances. The most important are the sulfonated alpha-olefins (TO THE), which are alternative replacements for LABS and AES, and sulfonated fatty acid methyl esters (FAME), which replace LABS.
Many other agents of an anionic or non-ionic nature are produced, which are used in household chemicals and cleaning agents.
The more important ones include non-ionic alkyl polyglucosides, which are characterized by very good surfactant properties, high wettability and foaming ability, compatibility with other SPCs and a very gentle effect on the skin. They are recommended for the production of dishwashing agents, washing powders and liquid cleaners.
Agents of an anionic nature are sulfonated paraffins (secondary alkyl sulfonates) used in the production of washing powders, washing liquids, cleaning, washing, shampoos, sulfosuccinates used in laundry compositions, cleansers and shampoos, isothioates used as mild agents in cosmetics, toilet and liquid soaps, taurates used in shampoos and lotions and sarcosinates used in shampoos, toothpaste, wool detergents and carpet cleaners.
In addition to the anionic and cationic SPCs, a group of amphoteric SPCs is distinguished. These agents contain both anionic and cationic compounds. Betaines are among the most common amphoteric SPCs, used in shampoos and liquid soaps, additionally having antifungal and antibacterial properties, and much smaller amounts of amino carboxylic acids, often used in shampoos, also characterized by bactericidal properties.
In order to obtain the best effect of removing various types of dirt from a specific type of materials, the laundry detergents often contain compositions of two, and sometimes several SPCs. The choice of the best SPCs depends largely on their impact on the human body, and also on the environment, due to the ease and degree of biodegradation.
SPCs are also used as emulsifiers in the production of pesticides, in cosmetics and household chemicals, as emollients, antistatic, corrosion inhibitors and are used in the cosmetics industry, textile, leather, stationery, cement, metal, in oil drilling and many other fields.