 Types of washing agents
Types of washing agents
Detergents, i.e.. substances, whose aqueous solutions have the ability to remove dirt, is used for washing and washing.
■ Detergents, due to the raw materials used and the degree of their processing, is divided into three basic groups:
• natural detergents of plant origin (np. saponina) and animal (np. enzyme concentrates from the secretions of animal glands);
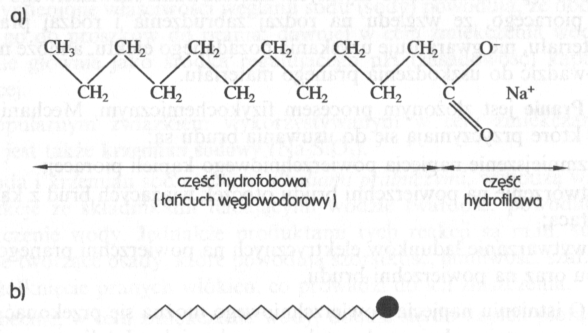
• soap obtained by saponification of natural vegetable and animal fats;
• synthetic detergents (detergents) obtained by chemical synthesis from various raw materials.
There are a lot of synthetic detergents, which differ in chemical structure, properties and scope of application. Taking into account the chemical structure, Synthetic washing agents can be divided into ions that dissociate in water, so-called. ionic, and non-dissociative, so-called. non-ionic. Ionic detergents, in turn, are divided into anionic (anionic, anionically active) i cationic (cation-active, cationically active).
Anionic detergents disintegrate while dissociating, forming a large anion, which has surfactant properties and an inactive cation (hydrogen or alkali metal). Their characteristic feature is the presence of negatively charged hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups in the active anion (carboxylic COO–, sulfate SPA3–, sulfone SO3– or others). Anionic detergents are excellent detergents and are among the most popular all synthetic detergents. They include several types of relationship, of which the most important are: alkyl sulfates, alkilosulfoniany i alkiloarylosulfoniany.
Cationic detergents, as a result of dissociation, split off a large surface-active cation and a non-surface-active anion (Cl–, Br–, J–, SO42-). The active cation contains a hydrophobic group and a positively charged hydrophilic group. Cationic detergents are the salts of aliphatic amines and aliphatic ammonium bases. The importance of this group of detergents is much less, due to the relatively low washing capacity.
Non-ionic detergents dissolve in water due to the presence of ether and hydroxyl hydrophytic groups. They have very valuable properties: high washing capacity, the ability to prevent dirt from re-depositing on the fabric, good emulsifying properties, wetting agents, they are stable in hard water, insensitive to the pH of the washing bath, have the ability to combine with most dyes and other chemicals. As a result, non-ionic detergents are now widely used, also in compositions with anionic detergents.
Washing agents, due to their intended use and application, can be divided into:
• laundry washing agents (vegetable fiber products), so soaps and other alkaline compounds, used for washing in a hot bath;
• detergents for washing delicate fabrics, showing good washing properties at lower temperatures (ok. 30 —40°C);
• wool products, neutral or slightly acidic;
• self-washing agents, np. enzymatic.
Surfactants are used both in the production of washing agents, cleaning, as well as for the production of personal care products, and also as emulsifiers. They are used mainly in the textile industry, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, laundry, tanning, dyeing and many others.